Linear Gaussian CPD¶
- class pgmpy.factors.continuous.LinearGaussianCPD.LinearGaussianCPD(variable, beta, std, evidence=[])[source]¶
Defines a Linear Gaussian CPD.
- The Linear Gaussian CPD makes the following assumptions [1]:
The variable is Gaussian/Normally distributed.
- The mean of the variable depends on the values of the parents and the
intercept term.
The variance is independent of other variables.
For example,
p(Y|X) = N(0.9 - 2x; 1)
Here, 0.9 - 2x is the mean of the variable
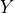 and the
standard deviation is 1.
and the
standard deviation is 1.In generalized terms, let
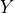 be a Gaussian variable with parents
X_1, X_2, \cdots, X_k. Assuming linear relationship between Y and
mathbf{X}, the conditional distribution of Y can be defined as:
be a Gaussian variable with parents
X_1, X_2, \cdots, X_k. Assuming linear relationship between Y and
mathbf{X}, the conditional distribution of Y can be defined as:p(Y |x1, x2, ..., xk) = \mathcal{N}(\beta_0 + x1*\beta_1 + ......... + xk*\beta_k ; \sigma)
References
- Parameters:
variable (any hashable python object) – The variable whose CPD is defined.
beta (list (array-like)) – The coefficients corresponding to each of the evidence variable. The first term of the beta array is the intercept term.
std (float) – The standard deviation of variable.
evidence (iterator (array-like)) – List of parents/evidence variables of variable. The order in which evidence is specified should match the order of beta.
Examples
# To represent the conditional distribution, P(Y| X1, X2, X3) = N(0.2 - 2*x1 + 3*x2 + 7*x3 ; 9.6), we can write:
>>> from pgmpy.factors.continuous import LinearGaussianCPD >>> cpd = LinearGaussianCPD( ... variable="Y", beta=[0.2, -2, 3, 7], std=9.6, evidence=["X1", "X2", "X3"] ... ) >>> cpd.variable 'Y' >>> cpd.evidence ['X1', 'X2', 'X3'] >>> cpd.beta array([ 0.2, -2. , 3. , 7. ])
- copy()[source]¶
Returns a copy of the distribution.
- Returns:
LinearGaussianCPD
- Return type:
copy of the distribution
Examples
>>> from pgmpy.factors.continuous import LinearGaussianCPD >>> cpd = LinearGaussianCPD( ... variable="Y", beta=[0.2, -2, 3, 7], std=9.6, evidence=["X1", "X2", "X3"] ... ) >>> copy_cpd = cpd.copy() >>> copy_cpd.variable 'Y' >>> copy_cpd.evidence ['X1', 'X2', 'X3']
- static get_random(variable, evidence, loc=0.0, scale=1.0, seed=None)[source]¶
Generates a LinearGaussianCPD instance with random values on variable with parents/evidence evidence with beta and std sampled from loc and scale
- Parameters:
variable (str, int or any hashable python object.) – The variable on which to define the TabularCPD.
evidence (list, array-like) – A list of variable names which are the parents/evidence of variable.
loc (float) – The mean of the normal distribution from which the coefficients are sampled.
scale (float) – The standard deviation of the normal distribution from which the coefficients are sampled.
seed (int (default: None)) – The seed for the random number generator.
- Returns:
Random CPD – A LinearGaussianCPD object on variable with evidence as evidence with random values.
- Return type:
pgmpy.factors.continuous.LinearGaussianCPD
Examples
>>> from pgmpy.factors.continuous import LinearGaussianCPD >>> LinearGaussianCPD.get_random( ... variable="Income", ... evidence=["Age", "Experience"], ... loc=2.0, ... scale=0.5, ... seed=5, ... ) <LinearGaussianCPD: P(Income | Age, Experience) = N(1.338*Age + 1.876*Experience + 1.599; 2.21) at 0x...
